Enzyme Activity Calculation Formula
Enzyme Activity Calculation Formula. Enzyme activity one unit of enzyme activity (u) is defined as the amount of enzyme that is able to convert 1 mole of substrate to product in one minute. In mg per ml / 1000))

 Studies on β Galactosidase Isolated from Apricots from file.scirp.org
Studies on β Galactosidase Isolated from Apricots from file.scirp.orgSubstitute in the known values and calculate the rate. In the example above, the 'change' was the amount of. Likewise, people ask, how do you calculate the specific activity of an enzyme?
T is the time when the absorbance value changes from a 1 to a 2 (min); C 0 is the intercept of the standard curve;

In the example above, the 'change' was the amount of. Remember to blank with the appropriate blank before starting the second set of reactions.

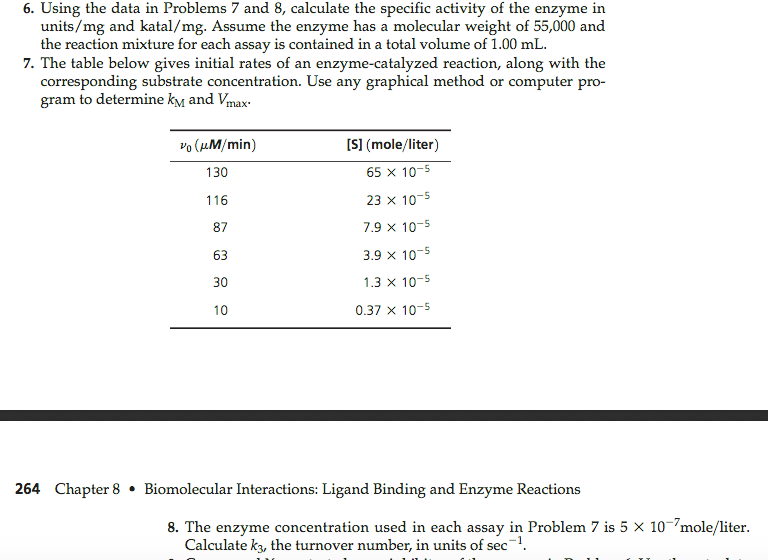
The profiles of enzyme reaction rate. To calculate the total diastatic power you can use either unit, as long as you are using the same unit.
Substitute in the known values and calculate the rate. Rate of change of abs per minute x (total reaction volume/ (ma/1000) x 1000/ (volume sample used) the ma term is the.
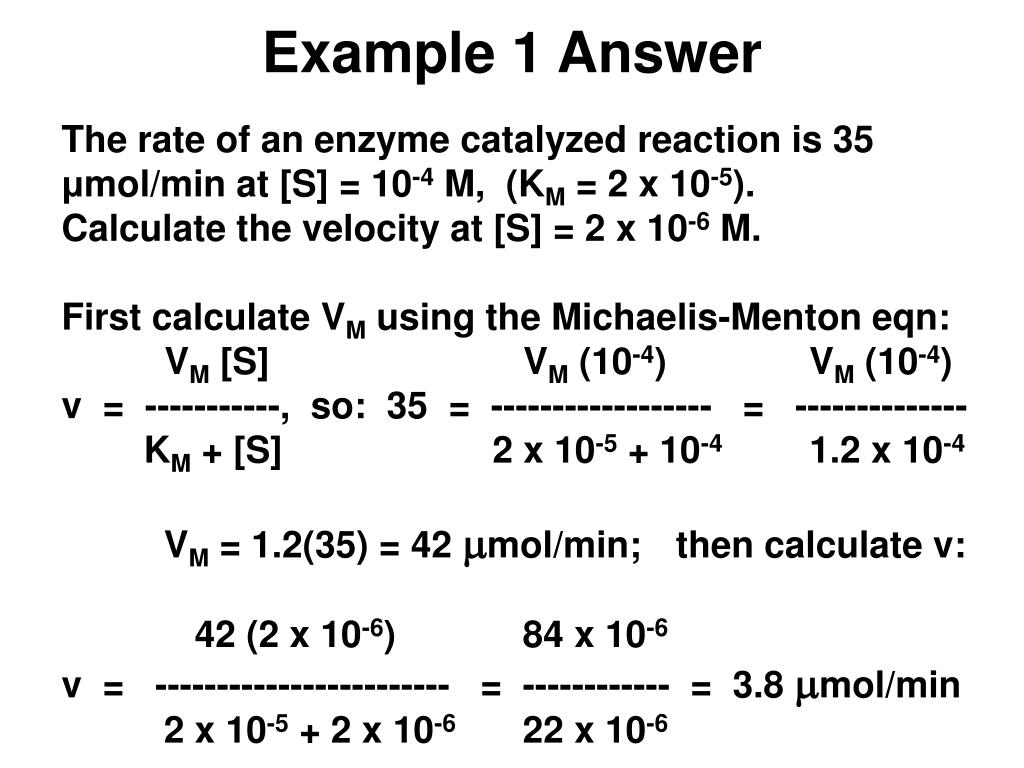
To convert one from the other, use the formula. It includes the concentration of enzyme by looking at vmax and another variable known as km or the michaelis constant.

Or the other way round. K is the slope of the standard curve;
Reaction sets tube/ label buffer (ml) enzyme extract (ml) distilled water (ml) 2.0ml dopa (keep on ice!) set 1: Rate = 7.5 g / hr or 7.5 g hr⁻¹.
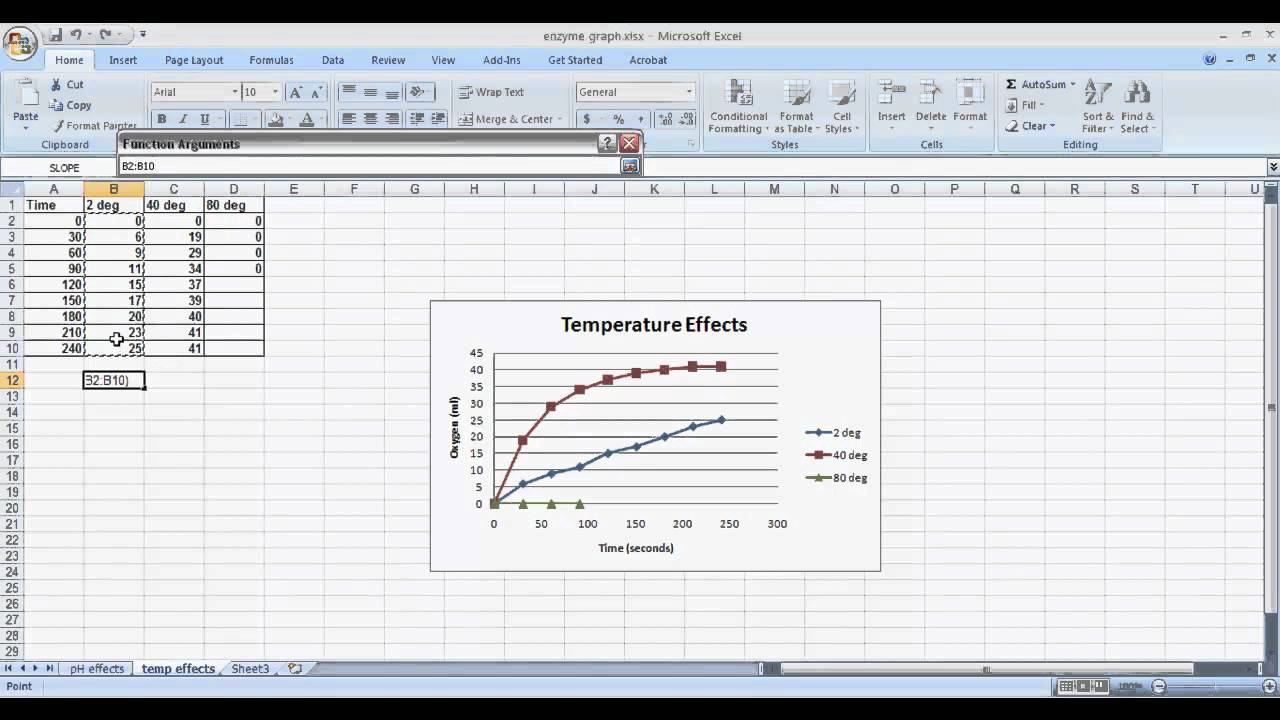
A 620 =(amplitude)e−(rate)*time for linear decay: Determine the rate of starch hydrolyses from the equation of your plot from #4.
Thus, 1 enzyme unit (u) = 1 μmol/min, where μmol refers to the amount of substrate converted. In µl x (protein conc.
Specific activity is units of activity/amount of enzyme (usually expressed in mg), ie. Include a polished plot with equation.

Thus, 1 enzyme unit (u) = 1 μmol/min, where μmol refers to the amount of substrate converted. That is what you present in your question.
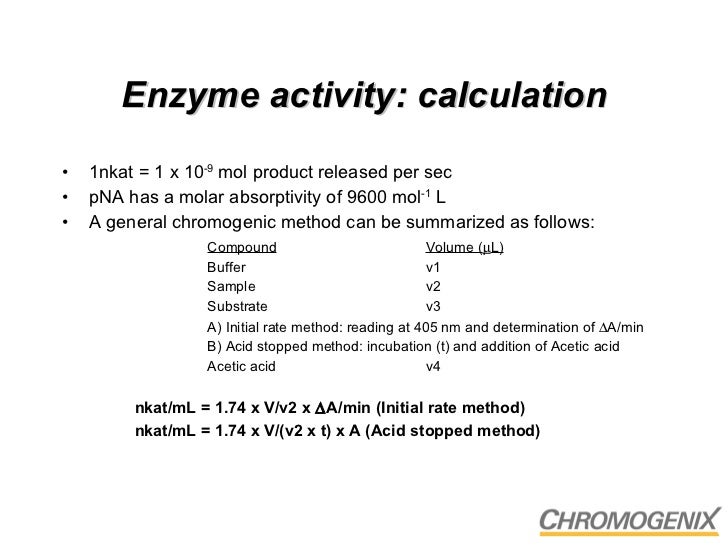
In summary, specific activity = enzyme units / (vol. So, the computation formula of enzyme activity is shown as formula :
(1) sod activity = a 0 − a 1 a 0 ÷ 50 % × system volume sample volume × dilution factor, where a 0 is the absorbance in the absence of sod, a 1 is the absorbance in the presence of sod,. The specific activity of the isolated enzyme was measured at 150 μmoles/min/mg protein before purification and 800.

Substitute in the known values and calculate the rate. In summary, specific activity = enzyme units / (vol.
Results and discussion the enzyme activities. A 620 =(amplitude)e−(rate)*time for linear decay:

Specific activity values are therefore quoted as units/mg or nmol/min/mg (if unit definition b is applied). Include a polished plot with equation.

Rate = 15 g ÷ 2 hours. Units x df x ml of stock protein solution = units

Therefore, specific activity is calculated by dividing the number of units/ml by the protein concentration in mg/ml to get μmol/min/mg. For soil assays, activity is reported as u per gram of dry soil.
A 620 =(amplitude)e−(rate)*time for linear decay: For soil assays, activity is reported as u per gram of dry soil.
Write out the equation for calculating the rate of enzyme activity. (2) where x is the laccase activity (μ g −1 );
Of Enzyme Activity, Detail The Methodology, And Discuss The Use Of High Throughput Techniques For Profiling Large Numbers Of Samples And Providing A First Step In The Process Of Identifying Potential Regulatory Candidates.T is the time when the absorbance value changes from a 1 to a 2 (min); Rate = change ÷ time (in this case, rate = amount of product formed ÷ time) step two: Units of activity (u) are typically used to describe enzyme catalytic activity, where a unit (u) refers to the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 1 micromole (μmole) of substrate per minute.
In The Indirect Sod Assay, Considering The Dilution In The Determination System, The Conventional Formula For The Calculation Of Sod Activity Presented By Absorbance Is Shown Below:Therefore, specific activity is calculated by dividing the number of units/ml by the protein concentration in mg/ml to get μmol/min/mg. (in this case, rate = amount of substrate used ÷ time) step two: To calculate the total diastatic power you can use either unit, as long as you are using the same unit.
Use Your Standard Curve Equation(we will use the cream ale recipe below as an example) total weight of grains in. Specific activity is units of activity/amount of enzyme (usually expressed in mg), ie. Units in the test = k × (∆a/min) where, k is 0.272 for catechol oxidase and 0.242 for laccase.
To Convert One From The Other, Use The Formula.In summary, specific activity = enzyme units / (vol. Rate of change of abs per minute x (total reaction volume/ (ma/1000) x 1000/ (volume sample used) the ma term is the. K is the slope of the standard curve;
Filter Paper Collapsing Method With The.0.2ml russet potato enzyme extract blank b1 2.6 0.2 2.0 0 The optimum ph is usually determined experimentally because of the difficulty in characterizing the active sites of enzyme. Rate = 7.5 g / hr or 7.5 g hr⁻¹.
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Enzyme Activity Calculation Formula"
Posting Komentar